Hands on demos
This document simple examples that are ready to use to test the differents protections or this Reference Architecture and capabiliites of the Fortigate to protect the cluster, apps and app traffic.
This is made to be fully compatible with AKS Tutorial and just add the security checks in-traffic provided by Fortigate. You can follow the Tutorial with or without this refarch.
Simple application internal LB and VIP
In applications folder you will find a ready to use azure voting app example based on Azure AKS tutorial. Simply run
kubectl apply -f applications/voting-app.yaml
You can check the yaml and see that we use the internal loadbalancer.
As a result once deployed:
azureuser@ftnt-demo-jumphost:~/secured-AKS-refarch$ kubectl get pods,svc
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
pod/azure-vote-back-6bdcb87f89-dt7cc 1/1 Running 0 4d10h
pod/azure-vote-front-5d6579c644-jwq5c 1/1 Running 0 4d10h
pod/azure-vote-front-5d6579c644-p4js9 1/1 Running 0 4d10h
NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE
service/azure-vote-back ClusterIP 10.8.112.42 <none> 6379/TCP 4d10h
service/azure-vote-front LoadBalancer 10.8.21.213 172.27.41.36 80:30924/TCP 4d10h
service/kubernetes ClusterIP 10.8.0.1 <none> 443/TCP 6d16h
In that case the IP to target is 172.27.41.36
Then on the fortigate set a VIP and port forward:
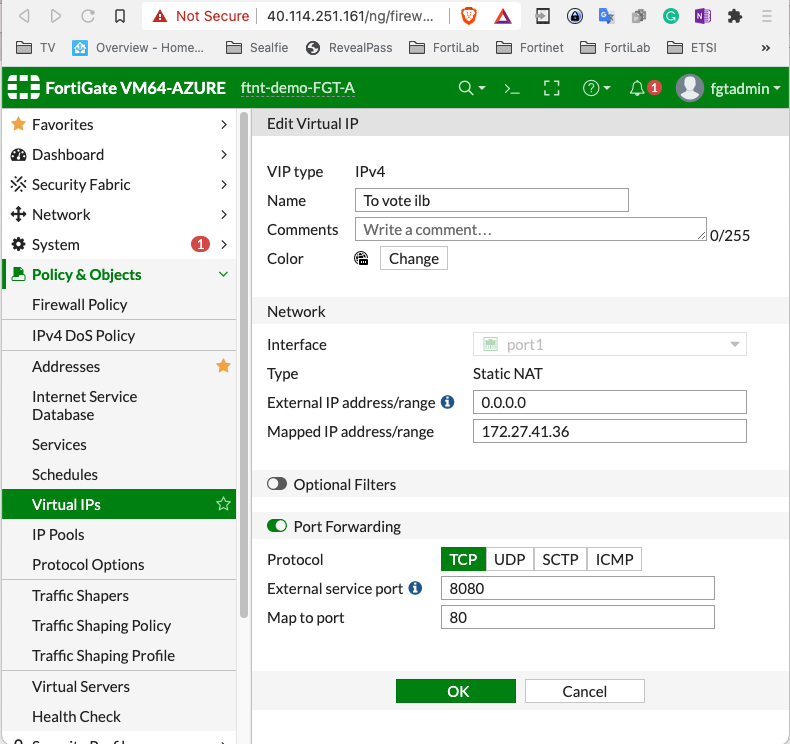
Add a firewall policy
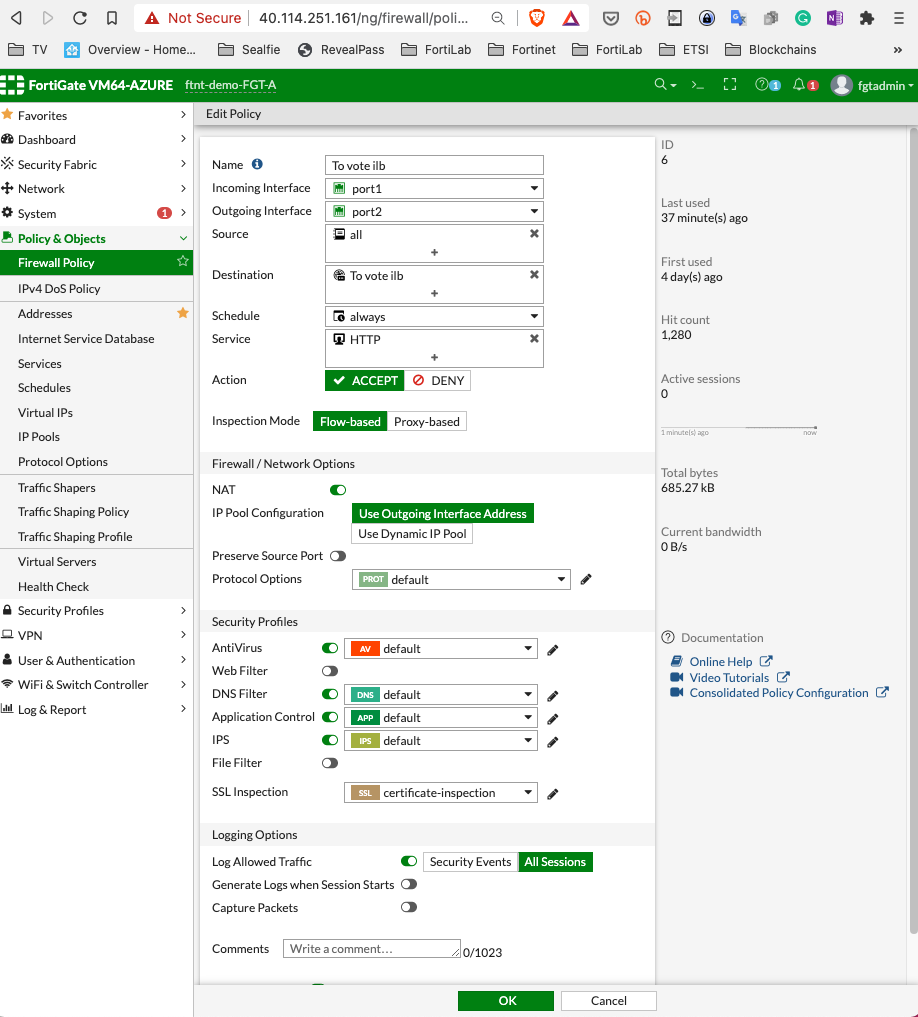
Of course adapt to your IP.
Using cli:
config firewall vip
edit "To vote ilb"
set mappedip "172.27.41.36"
set extintf "port1"
set portforward enable
set extport 8080
set mappedport 80
next
end
config firewall policy
edit 6
set name "To vote ilb"
set srcintf "port1"
set dstintf "port2"
set srcaddr "all"
set dstaddr "To vote ilb"
set action accept
set schedule "always"
set service "HTTP"
set utm-status enable
set ssl-ssh-profile "certificate-inspection"
set av-profile "default"
set dnsfilter-profile "default"
set ips-sensor "default"
set application-list "default"
set logtraffic all
set nat enable
next
end
You can now connect the http://<fgt IP>:8080 and it should like the following:
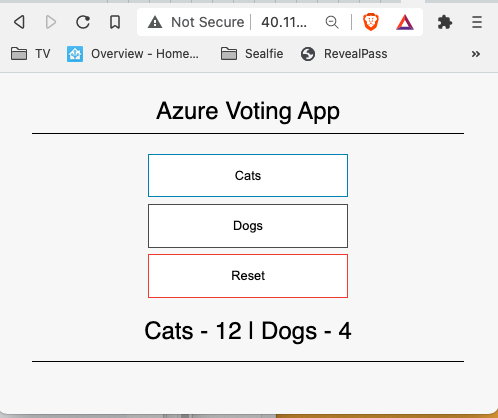
If using the VPN acces you can go directly to the internal load balancer IP.
To stress the system and see the Kubernetes autoscaling in action you can use:
ab -r -s 120 -c 500 -n 120000 -p vote.txt -T application/x-www-form-urlencoded -k http://<fgt IP>:8080
Wait a bit and monitor your number of pods.
The fortigate can then easily do the usual protection, DoS, and block known bad sites, limit repetitions etc..
Fortigate as a LoadBalancer
You can use the prototype code from https://github.com/fortinet/k8s-fortigate-ctrl to do even more advanced check on the fortigate. If commercially interested contact your Fortinet Rep. This one is alpha code.
Get the code an deploy the controller in K8S
git clone https://github.com/fortinet/k8s-fortigate-ctrl
cd k8s-fortigate-ctrl
kubectl apply -f fortigates.fortinet.com.yml -f lb-fgts.fortigates.fortinet.com.yml
kubectl create namespace fortinet
kubectl apply -n fortinet -f serviceaccount.yaml -f ctrl-role.yml -f rolebinding.yaml
kubectl -n fortinet apply -f deployment.yaml
To verify you can do:
kubectl get fortigates.fortinet.com fgt-az
NAME STATUS EXTERNALIP
fgt-az connected 40.114.251.161
Deploy or update the voting app:
kubectl apply -f examples/voting-app-antiaffinity.yaml
The only difference for the LoadBlancer is the annotation to use Fortigate controller: and look like this:
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: azure-vote-front
labels:
app: azure-vote-front
annotations:
lb-fgts.fortigates.fortinet.com/port: "90"
service.beta.kubernetes.io/azure-load-balancer-internal: "true"
spec:
type: LoadBalancer
# may try nodeport type to see if works better for K8S connector
ports:
- port: 80
selector:
app: azure-vote-front
You can access the app using http://<FGT public IP>:90/
See the LB CRD feedback
kubectl get lb-fgt
NAME STATUS FORTIGATE
azure-vote-front 1/1 fgt-az
The status represent the number of active health checks on the FGT versus number of target servers.
You make the FGT LB a TLS endpoint
kubectl edit lb-fgts.fortigates.fortinet.com azure-vote-front
in spec: section replace lb-type: http with lb-type: https
This allow to edit the created policy to do for example antivirus checks on random files uploaded to the Cluster or more advanced ips rules on the ingress traffic.
Tip
To have a nice monitoring of kubectl states
```shell script watch -c "kubectl get pods,lb-fgt,svc -o wide|ccze -A"
Use the ab command presented earlier to trigger autoscaling.
## Advanced debugging
Warning: **DO not do this in production please**
Connect with ssh [AKS nodes ssh access](https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/aks/ssh) (for debug)
SSH access to nodes for debug
Create a ssh keypair with ssh-keygen
If you deployed the windows nodepool you will need to change the kubectl run command from Azure page like this:
```shell
kubectl run -it aks-ssh --image=debian --overrides='{"apiVersion": "v1", "spec": {"nodeSelector": { "beta.kubernetes.io/os": "linux" }}}'
Nodes traffic
We now are going to enable the FGT K8S connector. You can go and do it yourself on th gui. Or use:
./ConfigureK8SConnector.sh
You receive a list of CLI to copy paste on the Fortigate, we cloud easily do an ansible playbook also. Once setup it should look like:
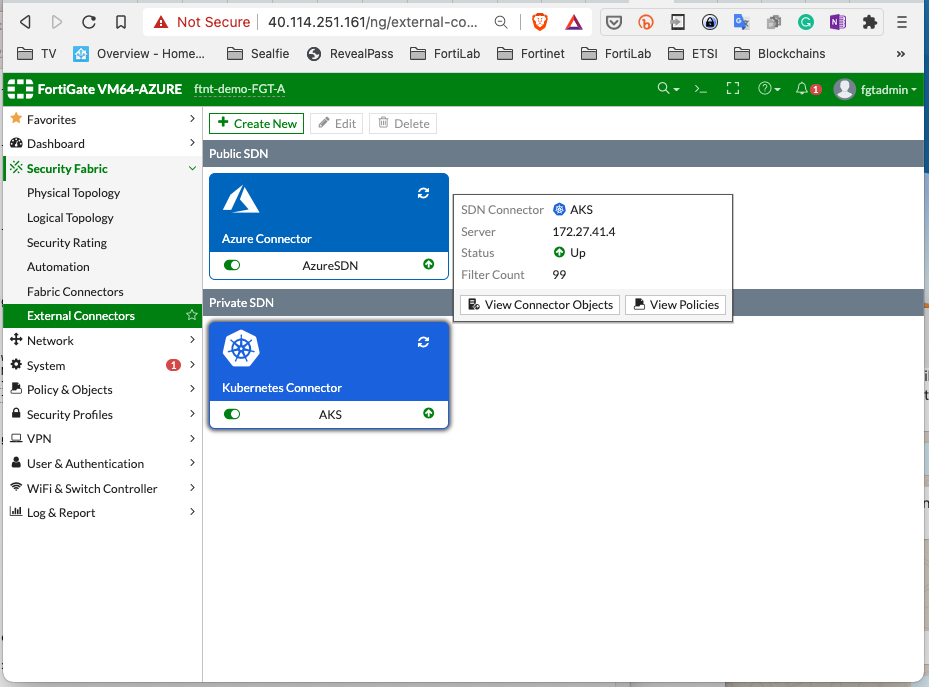
With the connector you can now create dynamic firewall objects.
config firewall address
edit "K8S nodes"
set type dynamic
set sdn "AKS"
set filter "K8S_Label.kubernetes.io/role=agent"
next
end
Will create a dynamic list of the Nodes VM ip only:
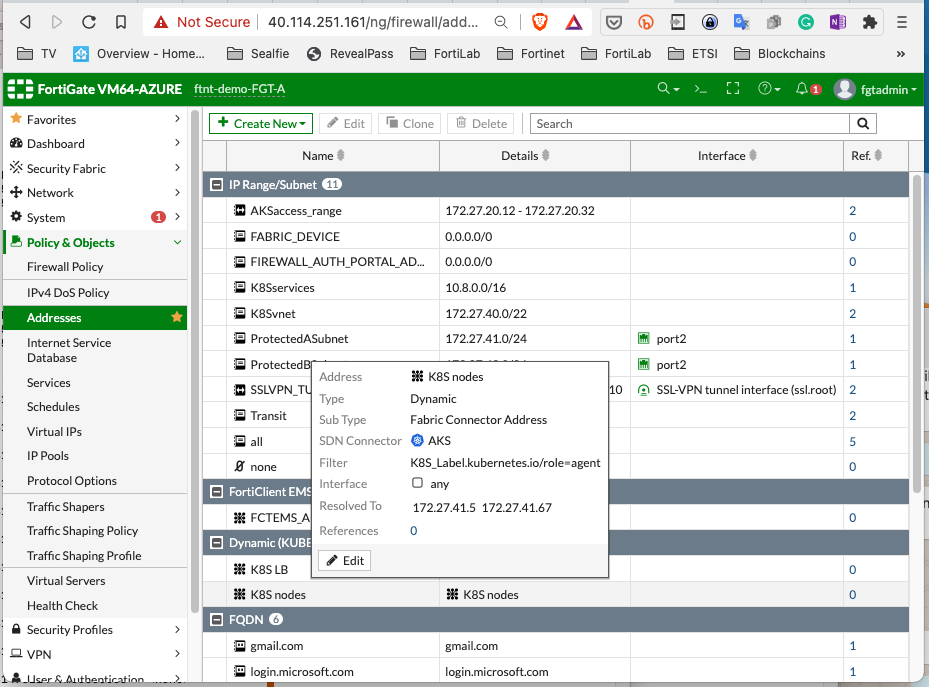
We can now for example create a specific policy linked to applications stearing to the traffic initiated on the nodes: *TODO
Antivirus
To have antivirus on the fortigate we must enable SSL inspection. On the fortigate go to "ProtectedSubnets-to-Internet" policy (this is the Egress traffic):
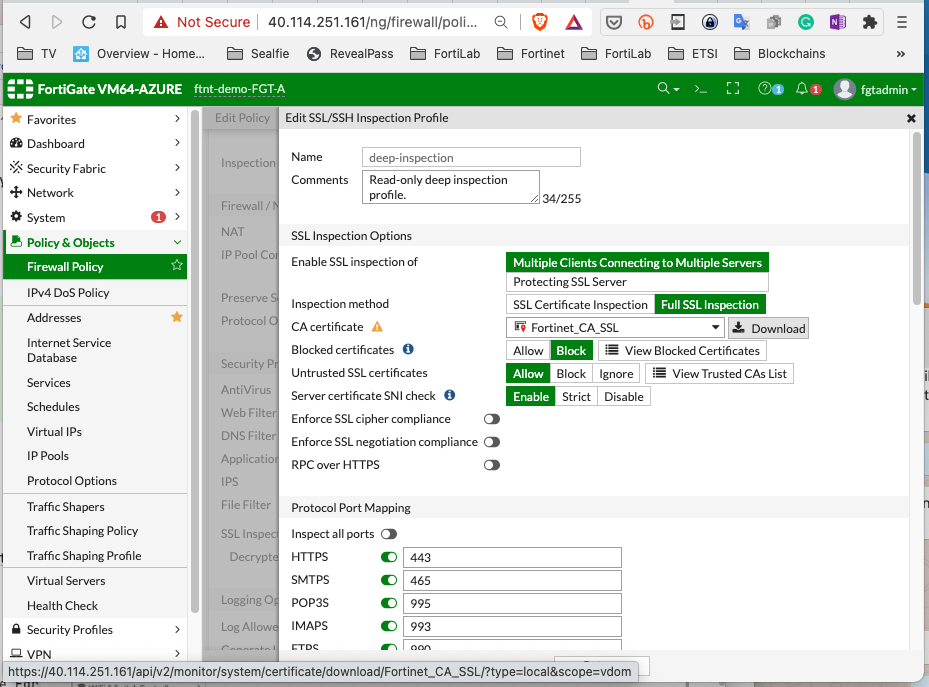
Download the file "Fortinet_CA_SSL.cer" then upload/put it where you run clis.
To move to the jumphost:
scp -P 2222 Fortinet_CA_SSL.cer azureuser@40.114.251.161:
Then make all you nodes trust the CA
./ConfigureK8SnodesCA.sh ~/Fortinet_CA_SSL.cer
Enable your Egress policy to use antivirus and deep inspection before next steps.
Test:
# a legite image:
kubectl run ub --image=ubuntu bash -it
Should work, you can exist and delete the pod.
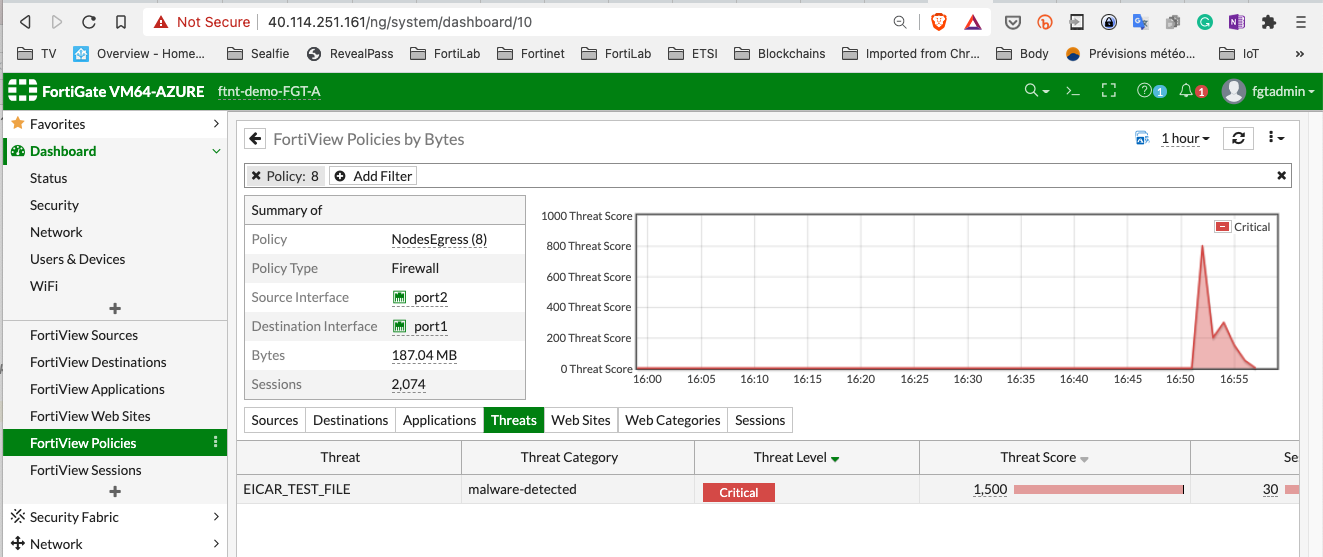
With an image containing a virus (EICAR is harmless)
kubectl run eicar --image=fortinetsolutioncse/ubuntu-eicar bash -it
You can see the source code of this in the project.
The second one should failed (timeout) you can get more details with kubectl describe pod eicar
And on the fortigate logs:
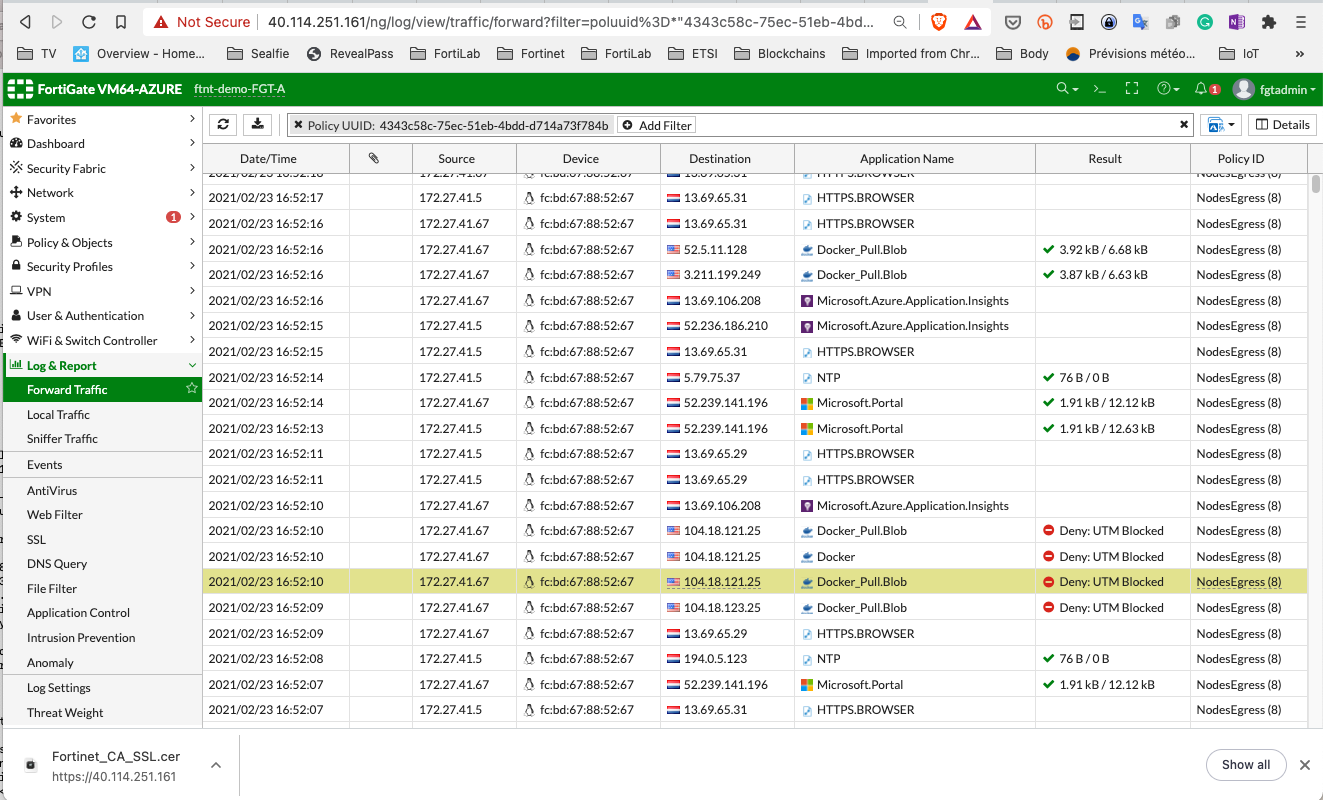
On fortiview panel in the fortigate: